
Navigating the complex world of healthcare insurance in the US can be challenging.
If you’re feeling overwhelmed, don’t worry – we’re here to help! Our beginner’s guide to understanding US healthcare insurance is designed to make this complex world a little easier for you.
From choosing the right healthcare insurance plan for your needs to understanding the terminology used in the industry, we’ve got you covered.
Read on to start your journey to better healthcare coverage today.
I. A Brief Overview of US Healthcare Insurance
Healthcare insurance is a crucial part of accessing healthcare in the US. It can impact everything from the cost of medical treatments to the choice of healthcare providers.
In this comprehensive US Healthcare Insurance 101 guide, you’ll find everything you need to know about coverage in America.
In this article, we will cover the different types of healthcare insurance plans available, including:
- Employer-sponsored insurance
- Private insurance
- Government-funded programs
We will also discuss:
- The various costs associated with healthcare insurance
- How to choose the right plan for your needs.
Why is understanding healthcare insurance important?

Understanding healthcare insurance is important because it affects not only your health but also your finances.
Medical expenses can be substantial. Your healthcare insurance can provide you with financial protection and peace of mind.
Staying up-to-date on the latest developments in the healthcare landscape is crucial, as these changes can have a significant impact on your coverage.
The purpose ad scope of this article is to demystify the US healthcare insurance system and help you navigate the complexities of healthcare insurance.
By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of healthcare insurance in the US, how to choose the right plan for your needs, and how to manage healthcare costs effectively.
II. Types of Healthcare Insurance Plans
With the wide range of healthcare insurance plans available, it can be challenging to make an informed decision about your healthcare coverage.
Healthcare insurance plans available in the US include employer-sponsored insurance, private insurance, government-funded programs like Medicare and Medicaid, and Marketplace plans.
Each type of plan has its benefits, costs, and eligibility criteria. Understanding the differences between these plans can help you choose the right one for your healthcare needs.
1. Employer-Sponsored Insurance
Employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) is a type of health insurance that is provided by an employer as a benefit to their employees. In ESI, the employer typically pays a portion of the premium, and the employee pays the remaining portion.
ESI is the most common form of healthcare coverage in the US, covering over 157 million people in 2019. ESI plans can vary widely in terms of coverage and cost, depending on the employer and the plan.
Typically, ESI plans provide access to a network of healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and other medical professionals. ESI plans may also offer additional benefits, such as dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage.
2. Private Insurance
Private insurance is a type of health insurance that is purchased directly by individuals or families. Unlike ESI plans, private insurance premiums are paid entirely by the insured.
Private insurance plans can be purchased from insurance companies, brokers, or the Health Insurance Marketplace established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Private insurance plans can vary widely in terms of cost and coverage. Plans may offer different levels of coverage, including Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum levels. Higher-level plans typically have higher premiums but offer more comprehensive coverage.
Private insurance plans also have a network of healthcare providers, and accessing out-of-network providers can result in higher out-of-pocket costs.
3. Government-Funded Programs
The US government funds several healthcare insurance programs to provide coverage to vulnerable populations. The two primary government-funded programs are Medicare and Medicaid, but there are also other programs, such as the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
Medicare:
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people over 65 and those with certain disabilities or chronic conditions.
Read more: Medicare 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Health Insurance for Seniors
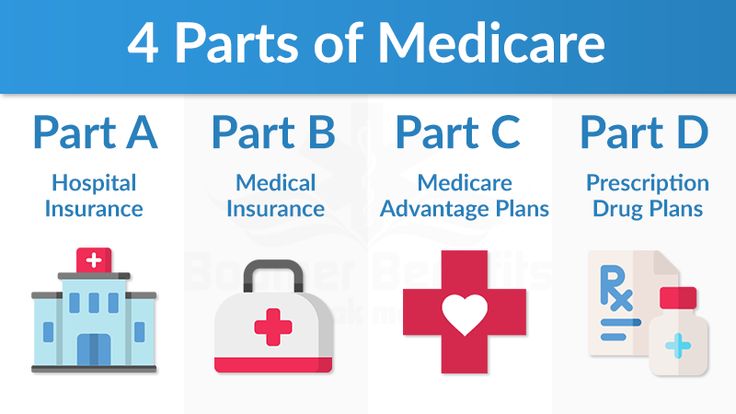
Medicare is divided into four parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D.
- Part A: covers hospitalization and inpatient care
- Part B: covers medical services and outpatient care
- Part C: also known as Medicare Advantage, is a managed care program that provides additional benefits
- Part D covers prescription drug coverage.
Medicaid:
Medicaid is a joint federal-state program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families.
Medicaid covers a wide range of services, including doctor visits, hospitalization, and prescription drugs. Eligibility for Medicaid varies by state and is based on income and other factors.
Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP):
CHIP is a collaborative program between the federal and state governments that offers healthcare coverage to children from low-income families who are not eligible for Medicaid.
CHIP covers a wide range of services, including doctor visits, dental care, and hospitalization. Eligibility for CHIP varies by state and is based on income and other factors.
4. Marketplace Plans
The Health Insurance Marketplace was established under the ACA to provide access to private insurance plans for individuals and small businesses.
Marketplace plans offer a range of coverage levels, and consumers can compare plans based on cost and coverage. Marketplace plans also provide financial assistance to eligible individuals to help offset the cost of premiums.
III. Understanding Healthcare Insurance Costs

Every healthcare insurance plan has its own set of advantages, expenses, and qualifications. Having a grasp on these costs will empower you to choose a plan that aligns with both your healthcare requirements and financial situation.
Here, we will discuss the various costs associated with healthcare insurance, including premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
1. Premiums
A premium is an amount you pay monthly, quarterly, or annually to maintain your healthcare insurance coverage.
The premium is determined based on various factors, including age, health status, location, and the type of plan you choose.
Employer-sponsored plans typically have a portion of the premium paid by the employer, while the employee pays the remaining portion. For private insurance and Marketplace plans, the premium is typically paid entirely by the insured.
2. Deductibles
A deductible is an amount you must pay out of pocket before your healthcare insurance coverage begins.
Deductibles vary based on the type of plan you have, with higher-deductible plans typically having lower premiums.
For example, a plan with a $1,000 deductible means you will pay the first $1,000 in healthcare costs before your insurance coverage begins.
Once you reach your deductible, your insurance coverage will begin, and you will pay a portion of the costs through co-pays or co-insurance.
3. Co-Pays:
A co-pay is a fixed amount you pay for a covered healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription medication.
Co-pays vary based on the type of plan you have, with higher co-pays typically associated with lower premiums.
For example, a plan with a $20 co-pay for a doctor’s visit means you will pay $20 for each visit, and your insurance will cover the rest of the cost.
4. Co-Insurance:
Co-insurance is the percentage of the cost you pay for a covered healthcare service after you have met your deductible.
For example, if you have a plan with a 20% co-insurance rate, you will pay 20% of the cost of a covered service, and your insurance will cover the remaining 80%.
5. Out-of-Pocket Maximum
An out-of-pocket maximum is the most you will pay out of pocket for covered healthcare services in a given year.
Once you reach your out-of-pocket maximum, your insurance will cover the remaining costs for covered services.
Out-of-pocket maximums vary based on the type of plan you have, and they can be quite high, especially for high-deductible plans.
IV. Choosing the Right Healthcare Insurance Plan
Selecting the right healthcare insurance plan requires careful consideration of certain factors such as your healthcare needs, prescription drug coverage, plan type, etc.
Taking the time to research and understand each factor will enable you to choose a plan that provides adequate coverage while minimizing your out-of-pocket costs.
Whether you’re shopping for a new plan or looking to make changes to an existing one, the tips and guidance in this section will help you make an informed decision and choose a plan that provides the coverage you need at a price you can afford.
7 Best Tips for Selecting the Right Health Insurance Plan for your Needs
Here are the key factors to consider when choosing your healthcare insurance plan:
1. Asses your Healthcare Needs
Assessing your healthcare needs is the first step in choosing the right healthcare insurance plan. Consider your medical history, current health status, and any ongoing medical conditions.
Evaluate the type of care you need, including preventive care, ongoing care, and any specialist visits or procedures. This information will help you determine the type of coverage you need and the level of benefits required.
For example, if you have a chronic condition that requires regular visits to a specialist, you’ll want a plan with a broad network of providers that covers the cost of specialist visits.
2. Determine Your Budget
Determine your budget for healthcare insurance premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Consider your income, other expenses, and any anticipated medical expenses. This will help you identify plans that fit within your budget and avoid plans that may lead to financial strain. Consider the monthly premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums when evaluating the cost of each plan.
For example, if you have a limited budget, you may want to choose a plan with a higher deductible and lower monthly premiums.
3. Consider Costs:
Consider the total costs of the plan. This includes monthly premiums, deductibles, co-pays, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. Evaluate the cost-sharing requirements for different services, such as specialist visits, lab tests, and hospitalization.
This will help you determine the overall cost of each plan and choose one that meets your budget and healthcare needs.
For example, if you require regular medical care, you may want a plan with lower co-pays and out-of-pocket maximums.
4. Your Preferred Network of Providers
Check whether your preferred healthcare providers, such as doctors and hospitals, are included in the plan’s network.
If your preferred providers are not included, you may need to switch providers or pay higher out-of-pocket costs.
Out-of-network providers can result in higher out-of-pocket costs, so it’s important to choose a plan that includes your preferred providers or a specialist you need to see. For example, if you have a strong relationship with your primary care physician and prefer to continue seeing them, you’ll want to choose a plan that includes them in their network.
5. Check Prescription Drug Coverage
If you take prescription medications, check the plan’s formulary, which is a list of covered medications. Evaluate whether your medications are covered and if there are any restrictions or requirements, such as prior authorization or step therapy.

The cost of prescription drugs can be significant, so it’s important to choose a plan that provides adequate coverage for your needs.
Consider the co-pays for your medications and any restrictions on the quantity or duration of your prescriptions. If you have expensive medications, you may want to consider a plan that offers lower co-pays or broader coverage.
If you require a specific medication that’s not covered by a plan, you may want to consider a different plan or explore alternative medication options.
6. Compare Plan Coverage
Compare the coverage of each plan you’re considering. Evaluate the benefits provided for preventive care, ongoing care, and any specialist visits or procedures you may require.
Consider the cost-sharing requirements for different services, such as co-pays, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. Ensure that the plan provides the coverage you need and that the cost-sharing requirements fit within your budget.
For example, if you require regular lab tests or imaging, you’ll want to choose a plan that covers these services at a reasonable cost.
7. Identify the Plan Options
The first step in comparing plans is to identify the available options.
Consider the plan type that best suits your needs. Employer-sponsored plans are typically the most common, but you may also consider private insurance, Marketplace plans, or government-funded programs like Medicare and Medicaid.
Each plan type has its eligibility criteria, costs, and benefits, and understanding these differences will help you choose the right plan.
For example, if you’re employed, evaluate the benefits provided by your employer-sponsored plan and compare them to individual plans available on the healthcare exchange.
8. Review Plan Summaries:
Once you have identified your plan options, review the plan summaries. Plan summaries provide an overview of the plan benefits, cost-sharing requirements, and network of providers. Ensure that you understand the coverage and cost-sharing requirements of each plan.
Reviewing the plan summaries can help you quickly eliminate plans that do not meet your needs.
For example, if you’re evaluating multiple plans, create a spreadsheet to compare the benefits and costs of each plan side by side.
9. Research Plan Quality
Research the quality of each plan you’re considering. Consider customer satisfaction ratings, quality of care ratings, and accreditation status.
These factors can provide insight into the level of care provided by each plan and the experience of other members.
For example, if a plan has consistently low customer satisfaction ratings, it may be an indication of poor service or limited coverage.
Consider the plan’s rating from organizations like the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) or the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
10. Financial Assistance
If you cannot afford healthcare insurance, check whether you are eligible for financial assistance.
Explore financial assistance options, such as subsidies or tax credits, that may be available to you. These options can help lower your monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Marketplace plans offer subsidies based on income levels, and government-funded programs like Medicare and Medicaid provide coverage for those who meet specific eligibility criteria.
Ensure that you understand the eligibility requirements and application process for each option. For example, if you have a limited income, you may qualify for a subsidy that can significantly reduce your monthly premiums.
11. Seek Expert Advice
If you’re feeling overwhelmed by the process of choosing a plan, a licensed insurance broker or healthcare navigator can provide personalized guidance and support to help you make an informed decision.
These professionals can provide guidance and support in choosing the right healthcare insurance plan. They can help you navigate the complex healthcare system, evaluate plan options, and determine eligibility for financial assistance.
V. Healthcare Insurance Enrollment and Renewal

Enrolling in and renewing healthcare insurance is an important process that ensures that you have adequate coverage for your healthcare needs.
It’s essential to understand the enrollment and renewal process to ensure that you don’t miss any important deadlines or opportunities to change your coverage.
Healthcare Insurance Enrollment:
Healthcare insurance enrollment is the process of selecting a healthcare insurance plan that meets your healthcare needs and budget.
1. Open Enrollment Periods
The open enrollment period is a specific time of year when individuals can sign up for healthcare insurance or change their existing plan.
The open enrollment period for healthcare insurance typically occurs between November 1st and December 15th, but the dates can vary depending on the type of plan and state.
During this period, you can explore different plan options, compare costs, and select a plan that meets your healthcare needs and budget.
2. Special Enrollment Periods
In some cases, you may qualify for a special enrollment period outside of the open enrollment period.
Qualifying life events that may trigger a special enrollment period include getting married or divorced, having a child, losing your job, or moving to a new state.
During a special enrollment period, you have 60 days to enroll in healthcare insurance or change your existing plan.
3. Automatic Enrollment and Renewal
If you’re already enrolled in healthcare insurance and you don’t take any action during the open enrollment period, you may be automatically enrolled in the same plan for the upcoming year. This is known as an automatic renewal.
However, it’s important to review your current plan to ensure that it still meets your healthcare needs and budget.

Healthcare Insurance Renewal
Healthcare insurance renewal is the process of re-enrolling your existing healthcare insurance plan for another year.
If you’re happy with your current plan and want to keep the same coverage for the upcoming year, you can renew your plan during the open enrollment period. However, it’s important to review your current plan to ensure that it still meets your healthcare needs and budget.
During the healthcare insurance renewal process, you should review your plan benefits, cost-sharing requirements, and network of providers. Evaluate whether your plan still provides adequate coverage for your healthcare needs and whether the cost-sharing requirements fit within your budget.
If you’re unhappy with your current plan or your healthcare needs have changed, you can explore different plan options and enroll in a new plan during the open enrollment period.
How to Enroll or Renew Your Healthcare Insurance
During the open enrollment period, you can enroll in or renew your healthcare insurance coverage through the federal or state healthcare exchange, or through a private insurance company.
To enroll, you’ll need to provide personal and financial information, such as your income, household size, and healthcare needs.
Once you’ve enrolled, you’ll receive confirmation of your coverage and the associated costs.

Navigating the healthcare system can be a complex and overwhelming experience, especially for those who are new to the system or have limited healthcare knowledge.
Here are some key points to consider when navigating the healthcare system:
1. Understanding Healthcare Terminology
The healthcare system can be filled with complex medical terminology that can be difficult to understand.
It’s important to take the time to learn and understand key terms and medical jargon that can help you make informed decisions about your healthcare.
This can include understanding terms like deductible, co-pay, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximum, as well as common medical terms related to diagnoses and treatments.
2. Finding a Healthcare Provider
Choosing a healthcare provider can be a daunting task, but it’s important to find a provider who meets your healthcare needs and preferences.
This can include factors such as proximity to your home or workplace, availability of services and treatments, and compatibility with your insurance plan.
You may also want to consider factors such as the provider’s experience, training, and specialty.
3. Understanding Healthcare Costs
Healthcare costs can vary widely depending on the provider, treatment, and insurance plan.
It’s important to understand the costs associated with your healthcare services, including deductibles, co-pays, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums.
You may also want to explore options for financial assistance or payment plans if you’re unable to afford the costs of your healthcare services.
4. Advocating for Your Healthcare Needs
As a patient, it’s important to advocate for your healthcare needs and ensure that you’re receiving the best possible care.
This can include asking questions about your diagnosis and treatment options, seeking second opinions, and being proactive in managing your healthcare.
You may also want to explore resources such as patient advocacy organizations that can provide support and guidance throughout your healthcare journey.

For example:
You are a new healthcare insurance policyholder who has been diagnosed with a chronic health condition. You are overwhelmed by the complexity of the healthcare system. You are unsure of how to navigate your healthcare needs. You should take the following steps to navigate the healthcare system:
- You start by researching key healthcare terms and jargon to better understand your healthcare insurance coverage and cost-sharing requirements.
- You use your insurance company’s online directory to find a healthcare provider who specializes in treating your specific condition and is in-network with your insurance plan.
- You compare the costs associated with different treatment options and explore options for financial assistance to help cover the costs of your healthcare services.
- You advocate for your healthcare needs by asking questions about your diagnosis and treatment options, seeking second opinions, and being proactive in managing your healthcare. You also join a patient advocacy organization that provides support and resources for patients with your condition.
VII. Healthcare Insurance and Life Changes
Life changes can have a significant impact on your healthcare insurance.
How to handle life changes that affect healthcare insurance
Here are some steps you can take to handle life changes that affect your healthcare insurance:
1. Review Your Current Healthcare Insurance Plan
The first step in handling a life change that affects your healthcare insurance is to review your current plan.
This includes understanding your current coverage, benefits, costs, and provider network. You should also review your plan documents to understand the rules for making changes to your plan.
2. Understand the Impact of the Life Change on Your Healthcare Insurance
The next step is to understand how the life change will impact your healthcare insurance.
Some life changes, such as a change in employment status or a move to a new state, may require you to enroll in a new healthcare insurance plan.
Other life changes, such as a change in income or family size, may impact your eligibility for government-sponsored healthcare programs or premium tax credits.
3. Update Your Healthcare Insurance Plan
Once you understand the impact of the life change on your healthcare insurance, you should take steps to update your plan.
This may include enrolling in a new healthcare insurance plan, updating your income information to ensure that you receive the appropriate financial assistance, or adding or removing dependents from your plan.
4. Know the Deadlines
It’s important to know the deadlines for making changes to your healthcare insurance plan.
For example, if you experience a qualifying life event, you may have a special enrollment period to enroll in a new healthcare insurance plan or make changes to your current plan.
You should also be aware of the open enrollment period for your healthcare insurance plan and make changes during this time if necessary.
Changes in Family Size
Changes in family size can have a significant impact on your healthcare insurance. Here are some steps you can take to handle life changes that affect your healthcare insurance due to changes in family size:
1. Understand Your Healthcare Insurance Plan
The first step is to understand your current healthcare insurance plan. Review your plan documents to understand your coverage, benefits, costs, and provider network.
Understanding your plan is important because it can help you determine the impact of the change in family size on your coverage.
2. Determine Your Eligibility for Government-Sponsored Healthcare Programs
Changes in family size can impact your eligibility for government-sponsored healthcare programs like Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
You should check whether you are eligible for these programs and enroll as soon as possible.
3. Add or Remove Dependents from Your Plan
If you need to add or remove dependents from your healthcare insurance plan, you will need to make changes to your plan.
Contact your healthcare insurance provider to understand the process for making changes to your plan. Be sure to do this as soon as possible to ensure that your coverage remains in effect.
4. Getting Married
If you get married, you may want to consider combining healthcare insurance plans with your spouse. You should compare the costs and coverage of each plan to determine which one is the most suitable for both of you.
Some plans may offer a spousal discount, while others may require you to add your spouse to your plan during open enrollment.
5. Having a Baby
Having a baby is a significant life event that may impact your healthcare insurance. You may want to consider changing your healthcare plan to one that offers better maternity benefits or pediatric care.
If you’re enrolled in a plan through the Affordable Care Act (ACA), having a baby qualifies you for a special enrollment period outside of the open enrollment period.
6. Turning 26
If you’re under 26 years old and covered by your parent’s healthcare insurance, you’ll lose your coverage when you turn 26.
You should review your options for healthcare insurance coverage, including enrolling in your employer’s plan or purchasing an individual healthcare plan through the ACA marketplace.
Changing Jobs
If you change jobs, you may lose your current healthcare insurance coverage.
You should review your options for healthcare insurance coverage through your new employer and compare them with other available plans.
If you’re unemployed, you may be eligible for Medicaid or other government-sponsored healthcare programs.
Changes in Income
Changes in income can also have a significant impact on your healthcare insurance.
Here are some important things to consider when experiencing changes in income and how they may impact your healthcare insurance:
1. Eligibility for Government-Sponsored Healthcare Programs
If you experience a decrease in income, you may become eligible for government-sponsored healthcare programs like Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
These programs offer low-cost or free healthcare coverage to individuals and families with limited income.
You should review your eligibility for these programs and consider enrolling if you meet the income requirements.
2. Eligibility for Premium Tax Credits
If you purchase healthcare insurance through the ACA marketplace, you may be eligible for premium tax credits based on your income. These tax credits can help lower your monthly healthcare insurance premiums.
If you experience a decrease in income, you should review your eligibility for premium tax credits and consider updating your income information on your healthcare insurance application.
3. Changes in Healthcare Plan Costs
Changes in income may also impact the costs of your healthcare insurance plan. If you experience an increase in income, you may become ineligible for premium tax credits and have to pay higher monthly premiums.
If you experience a decrease in income, you may become eligible for lower monthly premiums or cost-sharing reductions.
You should review your healthcare insurance plan costs and consider updating your income information if your income changes.
4. Reporting Changes in Income
It’s important to report changes in income to your healthcare insurance provider as soon as possible. This can help ensure that you receive the appropriate amount of financial assistance and avoid any unexpected costs or gaps in coverage.
You should also review your healthcare insurance plan costs and coverage each year during the open enrollment period to ensure that your plan still meets your healthcare needs.
Changes in Location
If you move to a new state, your healthcare insurance coverage may change.
You should review your options for healthcare insurance coverage in your new state and compare them with your current plan. You may also be eligible for a special enrollment period if you move outside of the open enrollment period.
Conclusion

Understanding healthcare insurance in the US is essential to ensure that you and your family have access to affordable and quality healthcare.
Here are some key points to remember:
- There are different types of healthcare insurance plans, each with its own costs, benefits, and limitations.
- When choosing a healthcare insurance plan, you should consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferred network of providers.
- Healthcare insurance enrollment and renewal are important processes that require attention to deadlines and eligibility criteria.
- Life changes, such as changes in income, family size, or health status, can impact your healthcare insurance and require adjustments to your plan.
To successfully navigate the US healthcare system, it’s important to stay informed and seek expert advice when needed.
You can find additional resources for further information and assistance by contacting your healthcare insurance provider, speaking with a healthcare insurance navigator, or visiting government-sponsored websites like Healthcare.gov.
In conclusion, understanding healthcare insurance in the US is a complex but critical task. By taking the time to educate yourself and make informed decisions about your healthcare insurance, you can ensure that you and your family have access to the care you need when you need it.
Disclaimer: This article does not offer any financial or personal advice. It is intended for informational purposes only. Rules and regulations of insurance policies may change, so please keep yourself updated as needed.
References:
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS): https://www.cms.gov/
- Healthcare.gov: https://www.healthcare.gov/
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): https://www.naic.org/
- American Medical Association (AMA): https://www.ama-assn.org/
- Kaiser Family Foundation: https://www.kff.org/
