
Worldwide, 1 in 3 women over 50 will experience osteoporotic fractures, as will 1 in 5 men. One in three hip fracture patients re-fracture at one year and over 1 in 2 will suffer another fracture within 5 years.
20-24 percent of hip fracture patients die within a year. Less than half of those who survive hip fractures regain their previous level of function.
Over 80% of all fractures in people over 50 are caused by osteoporosis. Worldwide, osteoporosis causes more than 8.9 million fractures annually, resulting in an osteoporotic fracture every 3 seconds. A prior fracture is associated with an 86% increased risk of another fracture.
These are some of the statistics published by the International Osteoporosis Foundation. Scary, aren’t they?
What is Osteoporosis?
The literal meaning of Osteoporosis is ‘porous bones.’ This is a disease that reduces the density and quality of your bones making them porous, fragile, and brittle. The deterioration of your bone tissue increases your risks of fracturing your bones, particularly of the wrists, hip, spine, and shoulder.
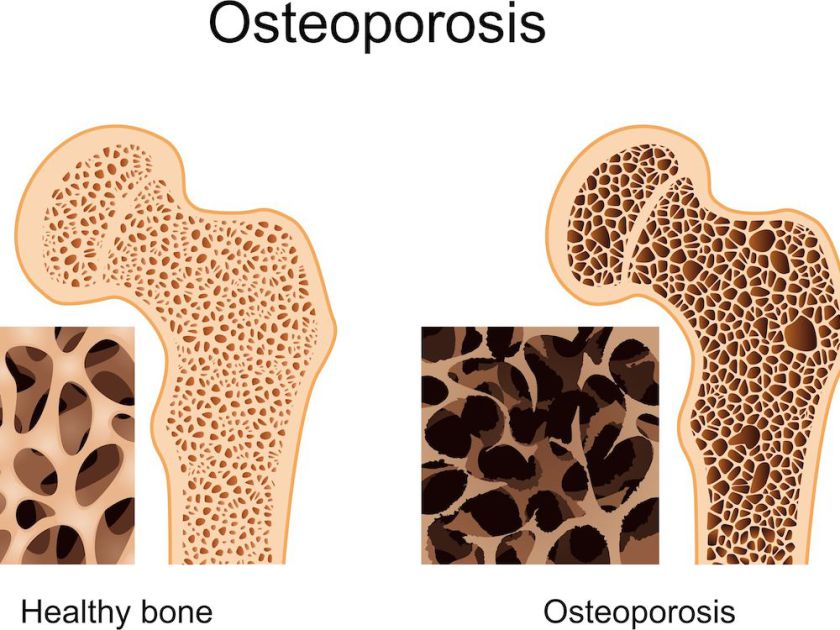
Osteoporosis is often referred to as “the silent killer” as the bone deterioration occurs silently and progressively. There are no symptoms and you get no warning… and then the first fateful fracture occurs, most often from a minor fall.
3 Factors that Increase the Risks of Osteoporosis
There are many factors that increase the risks of bone loss and osteoporosis. Age, sex, family history or genetics, ethnicity, and most important of all your diet, are various factors that contribute to your bone strength.
1. Age & Gender

Though it can happen at any age, the older you are, the greater is your risk of osteoporosis. Your bones are living tissue that is constantly changing. Till it reaches peak bone mass in the mid-twenties, a person’s bones continue to grow, develop and strengthen.
New bones cells regenerate to replace older cells that die naturally or due to injury. When bone loss outpaces the growth of new bone, osteoporosis develops.
Women are said to be at a higher risk for osteoporosis. Though the female hormone estrogen is said to protect the bones and lower the risk of osteoporosis, when the ladies hit menopause, the risk factor climbs tenfold. Their rate of bone loss increases dramatically. So it is vital that women take adequate precautions during this period to prevent osteoporosis.
2. Genetics and Ethnicity

Heredity is a very important risk factor for osteoporosis. If any family member has had an osteoporosis-related fracture, then it is said that your chances of getting a fracture doubles, regardless of your bone density.
Black and Hispanic women are believed to have lowered risk levels for osteoporosis while Caucasian and Asian women are more likely to develop the disease.
3. Various Lifestyle Factors
Heavy smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol, and lack of exercise are some lifestyle factors that contribute to bone deterioration and osteoporosis.

Maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for good bone health.
A high calcium diet is a must during pregnancy and while breastfeeding, to ensure the health of the mother as well as that of the infant. Inadequate nutrition in early childhood can result in weakened skeletal frames that are more prone to osteoporosis at later ages.
Read more: How Salmon Helps with Weight Loss and Helps you Look and Feel Better
