
The third most common health problem in the US, ‘hearing loss’ is a disorder that can affect the hearing of both children and adults.
Hearing loss refers to the diminished ability of a person to hear things – partially or totally. This usually results from sound signals not reaching the brain. Aging, long-term exposure to loud noises, trauma, diseases, certain medications, and heredity can all contribute to damaging our sense of hearing.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can range from mild or moderate to total deafness when the person cannot hear any sound at all, even at the loudest volumes. With mild to moderate hearing impairment a person may find it difficult to hold a conversation with friends, hear the doorbell, or the car honking on the road.
A person’s severity of hearing loss or the degree of hearing impairment is categorized by how much louder the sound volumes need to be set than the “usual levels” for these people to detect the sound.
Hearing loss is categorized into 3 main types depending on the physical location of the damage within the ear. A different type of hearing problem arises when a person’s brain is unable to process sound information, despite having perfectly working ears.
The four different types of hearing loss are:
- Auditory Processing Disorders
- Conductive Hearing Loss
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Mixed Hearing Loss
1. Central Auditory Processing Disorders
Central auditory processing disorder, more commonly called Auditory processing disorder or APD is a disorder that arises when the brain has trouble processing the auditory information it gets. Individuals suffering from APD have normal ear structure and function. Though they hear the information the same way as others, their brain has difficulty recognizing and interpreting sounds.
APD can affect people of any age. Though it can develop in adults, most cases begin in childhood. For many children suffering from APD, the symptoms may be obvious from a very young age, but for others, the symptoms become apparent only when they start school.
APD can affect a person’s ability to pinpoint the source of a sound and which sound comes before another. They have trouble remembering oral instructions. They find it difficult to understand the speech if a person speaks quickly, or if more than one person is speaking. APPD also interferes with their ability to enjoy music.
2. Conductive Hearing Loss
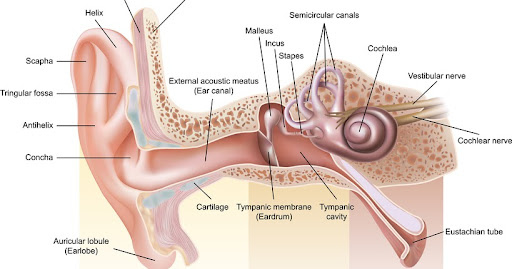
Conductive Hearing Loss occurs when sound waves are unable to reach the inner ear due to common causes like fluid or earwax buildup. Ear infections, a punctured eardrum, or Otosclerosis which is an abnormal bone growth in the Middle Ear are some of the more serious causes.
In the conductive hearing loss, the sound energy reaching the inner ear is less intense or loud than that in the original stimulus. Since the cause can usually be identified and treated, there is usually a complete or partial improvement in most conductive hearing loss cases.
Simple solutions like clearing up the ear wax can help solve most cases, while more advanced medical treatment or surgery may be needed to help restore more serious cases of conductive hearing loss. For partial improvement cases, hearing aids can help correct the remaining hearing loss effectively.
3. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The cochlea is a portion of the inner ear that receives sound in the form of vibrations, causing the hair cells to vibrate, and then these vibrations are converted into nerve impulses and sent to the brain via the auditory nerve for interpretation. Sensorineural hearing loss is a more permanent kind of hearing loss as the inner ear or the auditory nerve gets damaged in this case.
Though there are many possible causes of sensorineural hearing loss, natural aging is the most common cause. Noise-induced Hearing Loss is permanent hearing loss due to the damage from exposure to loud noises. Auditory Neuropathy results from damage to the auditory nerves that carry sound information to the brain. Diseases, accidents, and certain kinds of medications may also cause sensorineural hearing loss.
Just as in conductive hearing loss, the intensity of the sound is reduced in sensorineural hearing loss. Even when they are loud enough, there may be an added element of distortion in what is heard resulting in the sounds being unclear. The first step is to try out possible medical treatments. Once clear that the hearing loss is permanent, amplification through hearing aids can help reduce some of the effects of Sensorineural Hearing Loss.
Mixed Hearing Loss
When a person suffers from both Conductive Hearing Loss and Sensorineural Hearing Loss, it is called Mixed Hearing Loss. The sensorineural component is irreversible, while the conductive component may be treatable. This makes the hearing worse than having sensorineural loss alone.
When a person with Presbycusis [age-related sensorineural hearing loss] has a wax block in the ear, it causes a temporary case of mixed hearing loss. If the conductive component is due to an active ear infection, extra care must be taken to cure the infection before using hearing aids.
Conclusion
Hearing loss happens gradually and most people don’t become aware of their problem till it becomes quite extreme. But the problem is that the older generation tends to accept it as an inevitable part of aging and they don’t seek the help they need.
All hearing loss is not the same. Understanding the cause and the type of hearing loss goes a long way in helping to rectify the problem. It’s most important to get the correct diagnosis at the earliest and get the proper treatment to overcome the physical mental and emotional consequences of untreated hearing loss.
There are many digital solutions for those with hearing problems to improve their communication skills and their quality of life. You can find hearing aid-compatible mobile phones that are specially designed for the older generation. Senior-friendly telephones with extra-large keypads, big, bright displays, and amplified sound speakers make it easier for elderly people to communicate with their loved ones.
